
 Search
Search
 Dictionary
Dictionary
 Traffic
Traffic
 Map
Map
 Weather
Weather

| |
 Search
Search
 Dictionary
Dictionary
 Traffic
Traffic
 Map
Map
 Weather
Weather
|
| | Theme | Demo | Publication | Etc | Japanese | | ||
| |
 Soft Human-Interactive Robot, RI-MAN
Soft Human-Interactive Robot, RI-MAN
The bio-mimetic control research center of RIKEN is promoting basic research on the flexible and dynamic motor functions of biological systems. The goal is to create advanced engineering systems such as a soft human interactive robot. The robot developed here is named RI-MAN. RI-MAN exhibits the skill and ability to realize human care and welfare tasks. RI-MAN will become an invaluable partner robot. 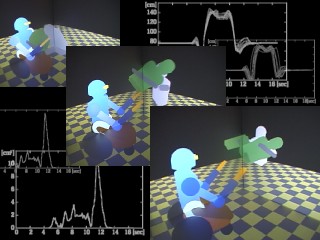 Cognitive Integrated Task Learning for Environmental Adaptive Robot
Cognitive Integrated Task Learning for Environmental Adaptive Robot
Recently, active researches have been performed to increase a robot's intelligence so as to realize the dexterous tasks in complex environment such as in the street or homes. However, since the skillful human-like task ability is so difficult to be formulated for the robot, not only the analytical and theoretical control researches but also the direct human motion mimetic approach is necessary. In this research, we propose that to realize the environmental interactive task, it is insufficient to replay the human motion along. We show a novel task learning approach to integrate the cognitive information into the mimic of human motions so as to realize the final complex task by the robot. As a detailed example of the task, we consider on how to carry up a human by cooperating two hands.  A 3D Interactive Dynamic Simulation Platform and
Its Application in Developing Human Friendly Robots
A 3D Interactive Dynamic Simulation Platform and
Its Application in Developing Human Friendly Robots
In this research, we construct a novel simulation environment for developing human interaction robot. This system uses AT-clone computers to calculate 3-dimensional dynamics and collision of a robot when it interacts with human and projects the audiovisual results using an immersion type display. Through dynamic calculation of the robot, human can interact with it directly in real time. This system makes it possible for us to design and examine the next generation of human interactive robot easily and safely. Experiments as a virtual robot interacts with human and performs dynamic motion show the effectiveness of our system.  Network-based Integration and Control of Decentralized Heterogeneous
Function Modules of a Dual-armed Redundant Robot
Network-based Integration and Control of Decentralized Heterogeneous
Function Modules of a Dual-armed Redundant Robot
An autonomous decentralized network control system of a robot is constructed via internet. This robot has totally 49 D.O.F. and can communicate with human to perform the required task based on its sound recognition and vision information. In order to realize real time control of so many D.O.F., 9 sets of AT-class PC are involved in controlling each module, such as a head, two arms and two multi-fingered hands, sound recognition and conversation as well as visual recognition. A server is used to coordinate the discrete events between each module. Bio-mimetic researches on hand preshaping when approaching to a specific object, as well as body languages with respect to the sound conversations are introduced into the system so as to realize the human friendly interaction. | |
| |
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
Top Page, Research at AIST, Research at Osaka Pref. Univ.
|
|

|